Copper uses
The many uses of copper
Copper is one of the world’s most important materials. According to the US Geological Survey, it ranks third among metals (after iron and aluminium) in terms of quantities consumed.
The use of copper is only going to increase as the world transitions to a circular economy in which recyclable materials are key.
Copper’s wide usage can be attributed to its impressive range of properties, which include:
- Electrical conductivity
- Thermal conductivity
- Corrosion resistance
- Anti-microbial properties
- Tough yet malleable
- Easy to join
- Easily and infinitely recyclable
- Strength and ductility in both high and low temperature uses
- Alloys well with other metals for a multitude of further applications
Reliable and versatile, copper has come to be relied upon in a variety of industries including plumbing, electronics and transportation.
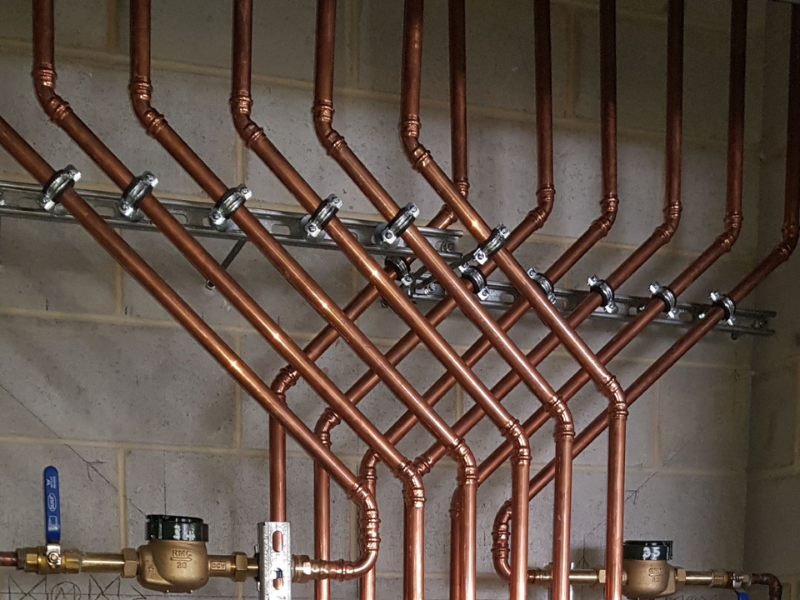
Copper pipes in plumbing
One of the oldest and most common uses of copper is plumbing. For centuries, copper plumbing pipes have been fitted in homes and workplaces with the purpose of transferring water and heat to taps and radiators.
Copper’s durability, malleability and natural resistance to corrosion makes it the material of choice for a wide range of pipework, including water pipes, radiator pipes and drainpipes. Copper pipes can even be found in modern air source heat pumps, owing to its excellent thermal conductivity.
Copper wires in electrical systems
Engineering applications for copper alloys are critical in the transition to clean power sources. According to the Copper Alliance, the generation of clean energy from solar and wind technologies has a copper usage that is typically 4–6 times more than fossil fuels.
Copper wiring is already becoming a vital component in powering the green energy revolution, whether used in the production of solar panels, wind turbines or rechargeable batteries found in electric vehicles.
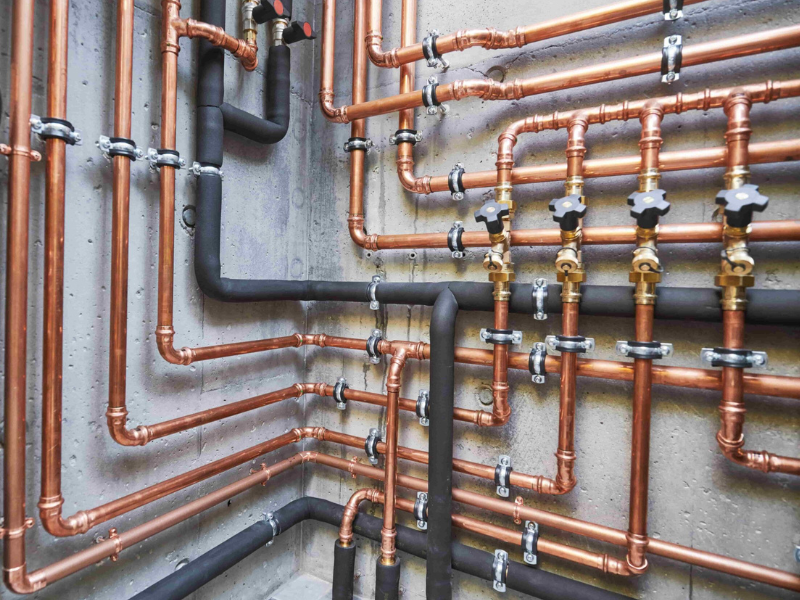

Copper pipes in hospitals
Besides being used to transfer heat and water around hospitals, copper pipes can also be found carrying medical gases like oxygen and nitrous oxide to patients during treatment.
Medical copper pipes can be trusted to deliver these vital medical gases without any risk of contamination. This is because copper is naturally antimicrobial, and therefore ensures medical gases remain sterile while on their way to patients.
Copper wires in transportation
Thanks to its high electrical conductivity and natural resistance to corrosion, copper is a key material in both cars and public transport. The metal is used in electric car chargers as well as the gearboxes, brake lines and cooling engines of petrol-based vehicles.
In terms of public transport, copper wiring is used to power train lines as well as the braking systems of buses and trains. Antimicrobial copper is also being used increasingly on high-touch surface on public transport systems to reduce the spread of viruses and diseases.

Other uses of copper
Elsewhere, the metal makes up part of Sweden’s nuclear waste handling technology, where copper canisters encapsulate the radioactive waste for long-term storage. The canisters are required to keep their integrity for at least 100,000 years but are thought to last five times that time.
Copper and its alloys are covered by national and international quality standards. In the UK and across Europe, designers, stockists and installers are safe in the knowledge that when they buy copper, they can be assured of high quality and defined mechanical standards.
This reliability has made it possible to innovate and break new ground in applications such as biological agriculture, powder metallurgy, architecture, automotive (EVs) and thousands of other industries.
With use in industrial products that need to keep their integrity for many decades, as well as domestic uses such as plumbing where they can last a lifetime, copper is a future-proof engineering solution and the material of choice for future generations.
Learn more about the uses of copper in construction and retrofitting
Frequently asked questions
What are some of the main uses of copper?
Copper is a versatile material that’s used widely across the electronics and plumbing industries. Copper wiring can be found in electronic devices like laptops and home appliances as well as rechargeable batteries and renewable energy systems, while copper plumbing pipes are used in many homes and workplaces.
How is copper used in wind turbines?
Copper is a key material for the power generators used in wind turbines. Lightweight and conductive, copper helps convert wind energy into electricity, and is also used in the wiring that transfers this energy down to the base of the tower. It’s estimated that a 3MW wind turbine contains up to 4.2 tonnes of copper.
How is copper used in solar panels?
Copper is used in the heat exchangers of solar panels as well as the wiring that transmits electricity to the grid, or to buildings that have solar panels installed. The metal’s high conductivity and resistance to corrosion make it a key material, with an estimated 5 tonnes of copper used per MW of power generation.
How is copper used in electric batteries?
Copper wiring is used in the batteries found in electric vehicles (EVs) and many portable electronic devices. The metal’s high electrical conductivity makes it suitable for use as an anode or cathode material. In addition, it’s used in the manufacture of EV motors, inverters and charging stations.
Why is copper used for electrical wiring?
Copper has a number of unique properties that make it especially suitable for electrical wiring. These include its durability, malleability and exceptional electrical conductivity, which means that electricity can pass through the metal more efficiently than most other conductors.
